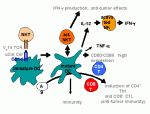
Current cancer vaccine strategies strive to efficiently deliver in situ immunogenic Tumour-Associated Antigens (TAAs) into functional Antigen-Presenting Cells (APCs). Stimulated APCs cells then initiate anti-tumour reactions through local and complex immune interactions targeting also the tumour microenvironment.
In this context, Xu et al. have recently developed a new effective oral cancer vaccine platform presenting potent immunogenicity and anti-tumour activity with long-lasting protective memory response (1).
The authors have designed optimized Salmonella-based vectors (Salmonella SPI2-encoded T3SS system) co-administrated with a Natural Killer (NKT) cells ligand (2). The delivery of heterogeneous TAAs into APCs has been proven to display enhanced anti-tumour activity through bacterial expressed TAAs-specific immune reponses.
Chemically synthesized NKT cells ligands (alpha-Galactosylceramide known as the αGalCer KRN7000 or alpha-GalCer) and its superior binding affinity analog 7DW8-5 were already known to enhance the immunogenicity and anti-tumour efficacy of bacterial vaccine vectors (3, 4). α-Gal-Cer is known to exhibit potent antitumor activity in various murine experimental cancer models.
Xu et al. clearly show here the potential interest of 7DW8-5 as a vaccine adjuvant in clinical tumour treatment with oral vaccines.

Sources:
- Xu et al. “Development of an Effective Cancer Vaccine Using Attenuated Salmonella and Type III Secretion System to Deliver Recombinant Tumor-Associated Antigens” (2014) Cancer Res Published Online First September 11, 2014. DOI:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-1169.
- Nicol A. et al. “Comparison of clinical and immunological effects of intravenous and intradermal administration of a-galactosylceramide (KRN7000)-pulsed dendritic cells” (2011) Clin Cancer Res, 1;17(15):5140-51. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-3105.
- Xiong G. et al. “Novel cancer vaccine based on genes of Salmonella pathogenicity island 2” (2010) Int J Cancer,126:2622-34. DOI: 10.1002/ijc.24957.
- Li X. et al. “Design of a potent CD1d-binding NKT cell ligand as a vaccine adjuvant” (2010) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010;107:13010-5. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1006662107.



