The treatment of diseases by inducing, enhancing, or surpressing an immune response is referred to as Immunotherapy. T-cell activation and inactivation requires the coordination of various co-inhibitory and co-stimulatory signals which are modulated by most immunotherapeutic approaches.
Therapeutic manipulation of immunopathways has lead to promising clinical results for the treatment of a number of diseases (ex. cancer, autoimmune diseases and inflammatory diseases…). Research projects in this field are rapidly evolving as scientists seek to identify the next generation of therapies.
In an earlier post on this blog, I introduced the latest advances regarding the the B7-1 : CD28 and B7-1 : CTLA4 pathways for immunotherapy screenings. Today, I’d like to focus on the PD-1/PD-L1/PD-L2 pathway.
After a brief review of the role of this pathway in immune response, let’s take a look at some of the screening tools I’ve selected (by our partner BPS Biosciences) to investigate this pathway for drug discovery applications. Interestingly, some of these tools are the first ready-to-use assay kits made available for drug discoverers to screen for inhibitors of the PD-1/PD-L1/PD-L2pathway.
Why look at PD-1/PD-L1/PD-L2 pathways in immunotherapeutics?
PD-1 is a receptor present on the surface of activated T-cells and other immune cells. PD-1 has two ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2, which are overexpressed in most human cancers. Binding of PD-L1 to PD-1 negatively regulates T cell signaling and inhibits cytotoxic T-cell activity.
Similarly, engagement of PD-1 by PD-L2 dramatically inhibits T-cell proliferation, especially in CD4+ (T helper) cells. Therefore, this upregulation of PD-L1 and PD-L2 may allow cancers to evade the host immune system.
Neutralizing antibodies can prevent PD-L1 from binding to PD-1 or to B7-1. Blockade of PD-L1 enables the activation of T-cells, restoring their ability to detect and attack tumor cells. Therefore a number of pharmaceutical companies are actively developing monoclonal antibodies targeting PD-1 and PD-L to boost the immune system for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer, melanoma, and bladder, renal, and triple-negative breast cancers.
The PD-1/PD-L pathway is also a therapeutic target for chronic viral-infections (including HIV and HCV). This therapeutic appraoch is based on the observation that PD-1 expression is upregulated by virus-specific T cells and that the inhibition of this loop is hoped to decrease viral load by increasing T cell function. Conversely, since the PD-1/PD-L interaction regulates self-tolerance and immunologic homeostasis, agonists of these proteins are promising drug targets for many autoimmune disorders including multiple sclerosis, arthritis, lupus, and type I diabetes.
The most advanced PD-1/PD-L1/PD-L2 screening reagents
These new therapeutical advances highlight the importance of reliable R&D tools in Drug discovery approaches and translation medicine programs. Access to robust research reagents covering the needs of Drug discoverers from target validation to screening (HTS or secondary) or even DMPK studies is crucial. Below, I’ve made a selection of some of the latest releases for scientists interested in the PD-1/PD-L1/PD-L2 pathway.
#1 – PD-1 – a receptor for PD-L1
PD-1 is the receptor for PD-L1. Formation of the receptor-ligand complex leads to an inhibitory signal which reduces proliferation of CD8x T cells.
PD-1 is available as a Fc Fusion (Id. nr 71106), as a FLAG-tagged variant (Id. nr 71115), and as a Biotin labeled variant (Id. nr 71109)
#2 – PD-L1 – a ligand for PD-1 receptor
PL-L1 is one of the ligands for PD-1, which plays a role in surpressing the immune response especially during pregnancy, tissue allografts, autoimmune diseases and diseases such as Hepatitis.
PL-L1 is available as a non labeled variant (Id. nr 71104) and a Biotin-labeled variant (Id. nr 71105).
#3 – PD-L2 – aligand for PD-2 receptor
PL-L2 is another ligand for PD-1 which, upon complex formation T cell proliferation, especially of CD4+ (T helper) cells, is dramatically decreased.
PL-L2 is available as a non labeled variant (Id. nr 71107) and a Biotin-labeled variant (Id. nr 71108).
#4 – PD1-neutralizing antibody
This antibody (Id. nr 71120) can be used as a control inhibitor using the PD-1:PD-L1[Biotinylated] Inhibitor Screening Assay Kit (see below).
Ready-to-use PD-1/PD-L1/PD-L2 screening assay kits
Recently, BPS Biosciences have released 3 unique ready-to-use assay kits to screen and profile inhibitors for the PD-1/PD-L1/PD-L2 signaling pathways
PD-1:PD-L1[Biotinylated] Inhibitor Screening Assay Kit (Id. nr 72003)
PD-1:PD-L2[Biotinylated] Inhibitor Screening Assay Kit Id. nr 72004)
Both are 96-well format assay kits and come with biotinylated PD-L1 or PD-L2, purified PD-1, streptavidin labeled HRP for 100 binding reactions.
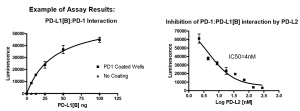
PD-L2 Inhibitor Screening Assay Kit (Id. nr 72006).
This 96-well format assay kits comes with biotinylated PD-1, purified PD-L2, streptavidin labeled HRP for 100 binding reactions.
Looking for PD-1/PD-L1/PD-L2 testings?
Choosing the right reagents or screening kits to raise the value of your compounds of interest by looking to PD-1/PD-L1/PD-L2 pathway can be challenging.
Research tools reviewed in this second post (belonging to a series of 3 posts dedicated to Immunotherapy screening) will definitely help you there. Otherwise, you can simply contact me with the form below.
[contact-form to=’Ali.el.baya@tebu-bio.com’ subject=’I am interested in Immunotherapy related screening products’][contact-field label=’Name’ type=’name’ required=’1’/][contact-field label=’Email’ type=’email’ required=’1’/][contact-field label=’Comment’ type=’textarea’ required=’1’/][/contact-form]
Recently released Immunotherapy Screening posts on the blog “being bio-reactive”:
Upcoming Immunotherapy Screening posts on the blog “being bio-reactive”:
- Immunotherapy Screening – Part 3: BLTA:HVEM and CD47:SIRPalpha Pathways




